4.
THE
GREENHOUSE EFFECT (I)
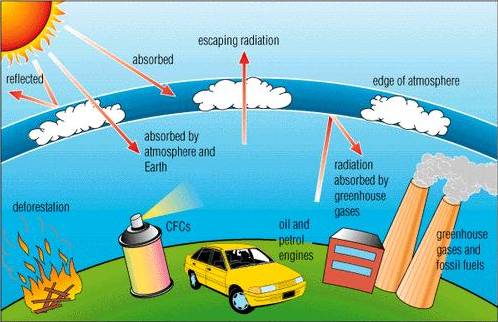
 Life on earth depends on energy from the sun. About 30 percent
of the sunlight that beams toward Earth is deflected by the
outer atmosphere and scattered back into space. The rest
reaches the planet’s surface and is reflected upward again as
a type of slow-moving energy called infrared radiation.
Life on earth depends on energy from the sun. About 30 percent
of the sunlight that beams toward Earth is deflected by the
outer atmosphere and scattered back into space. The rest
reaches the planet’s surface and is reflected upward again as
a type of slow-moving energy called infrared radiation.
As infrared
radiation is carried aloft by air currents, it is absorbed by
“greenhouse gases” such as water vapour, carbon dioxide, ozone
and methane, which slows its escape from the atmosphere.
TASK (Click
here)
|
