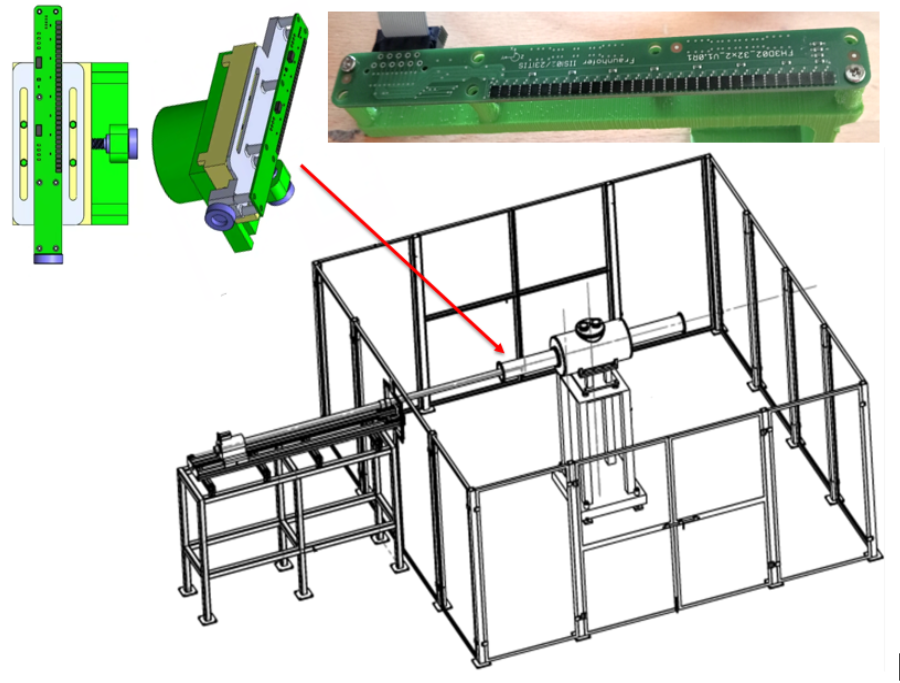
Magnetic Field Scanner System (MFSS)
The MFSS has been designed and built to perform 3D magnetic field mapping of the MAGDEM superconducting magnet and other components of the ISRS project. This high-precision system ensures compliance with stringent design specifications in terms of field quality and uniformity.
The MFSS consists of:
-
A multi-axis mechanical positioning system, capable of scanning volumes up to 1.7 meters with 0.05 mm precision (linear) and 1° angular resolution (rotational).
-
A HallinSight® 32×2 pixel 3D Hall sensor array, optimized for accurate magnetic flux density measurements.
-
An automated data acquisition and control software suite, developed in Python and Godot, enabling intuitive control, real-time monitoring, 3D visualisation, and data export.
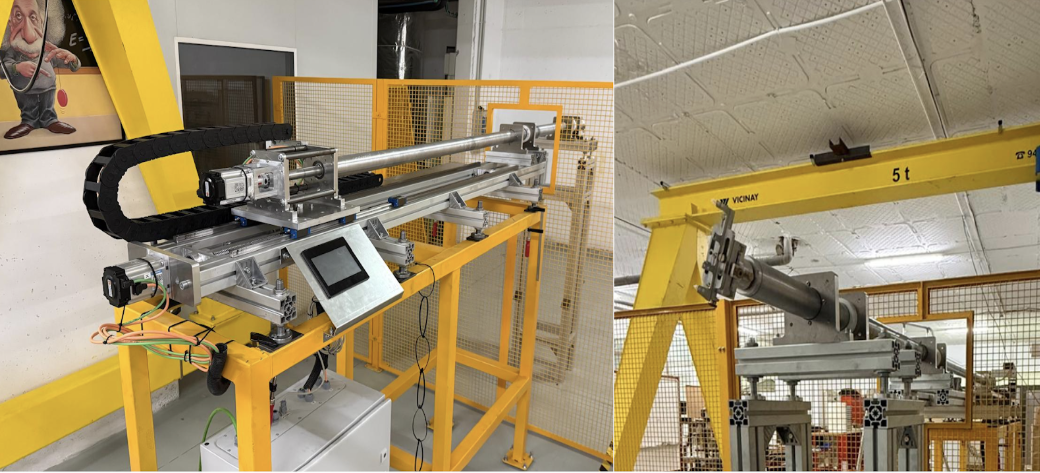
Figure 1. Sensor array, security area, and automated field mapping system. Each FH5401c unit contains two 3-D Hall sensors.
Main Features
- Non-magnetic mechanical structure to prevent interference with field measurements.
- Sensor alignment better than 2 mrad, ensuring high spatial accuracy.
- Magnetic resolution of 4 µT, with calibration accuracy of 0.2% in 15 mT fields.
- Safety perimeter, shielding, and a dedicated test zone at UHU.
Figure 2. Final MFSS system to be delivered at CERN/ISOLDE
Software Suite
Two software versions have been developed:
- Python GUI using Tkinter
- Godot interface with 3D vector rendering and G-code-based motor control
Functionalities include:
- Motor calibration and motion (linear & angular)
- Full 2D/3D scan capabilities
- Real-time visualisation and export (CSV/TXT)
- Visualization of Bx, By, Bz components and gradient maps
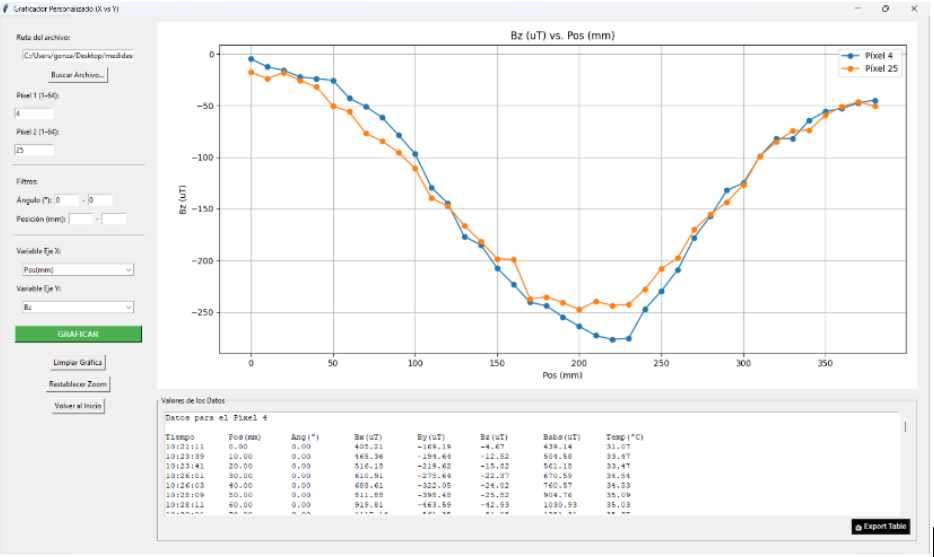
Figure 3. Users control interface. Plot of By and Bz components using the protype MFSS (Python).
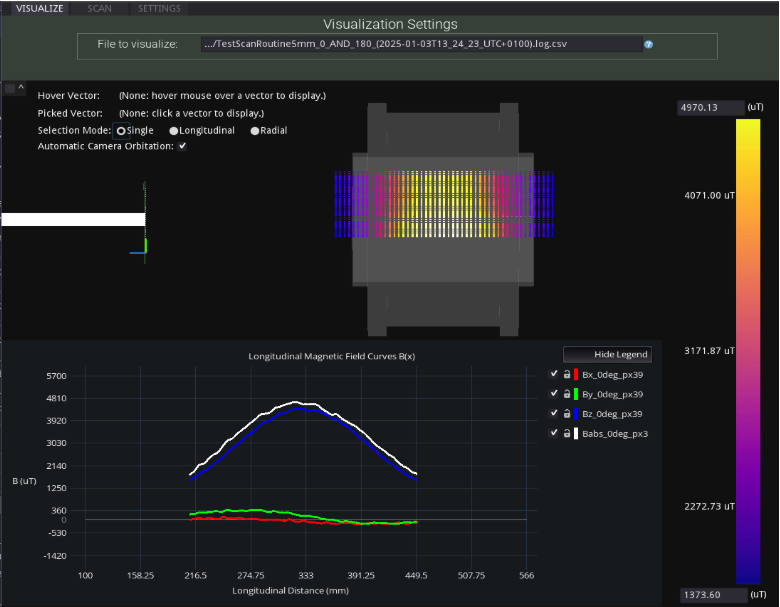
Figure 4. 3D visualization of Bx, By, Bz Babs using the protype MFSS (Godot).